
THORACIC EPIDURAL LIPOMATOSIS RADIOLOGY
OVERVIEW
Thoracic Epidural lipomatosis is not uncommon to see but has a different appearance to Lumbar Epidural Lipomatosis
WHAT IS THORACIC EPIDURAL LIPOMATOSIS?
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF EPIDURAL LIPOMATOSIS?
WHAT TO LOOK FOR: MRI OF THORACIC EPIDURAL LIPOMATOSIS
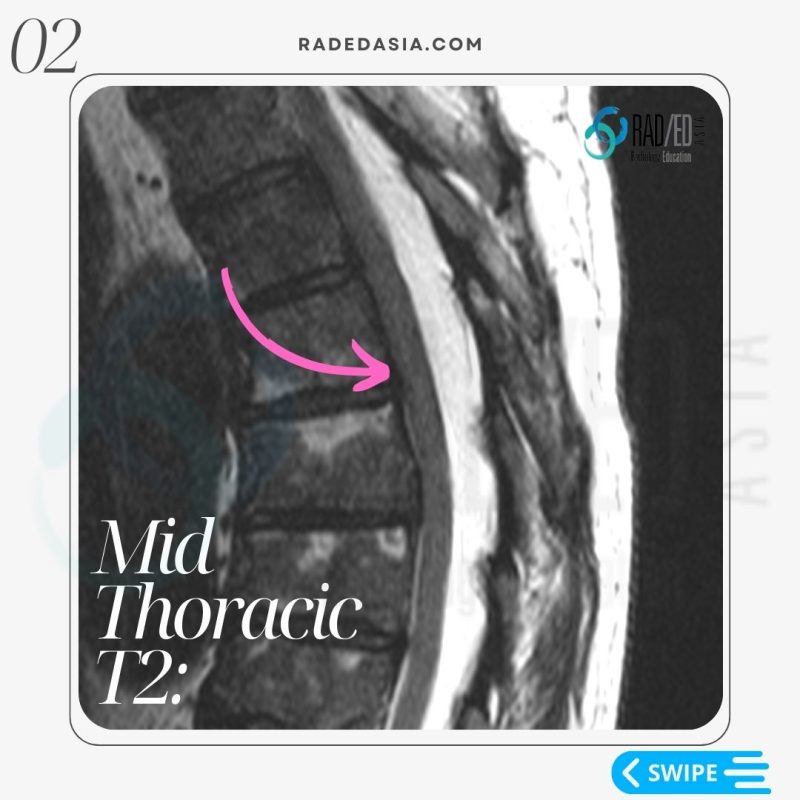
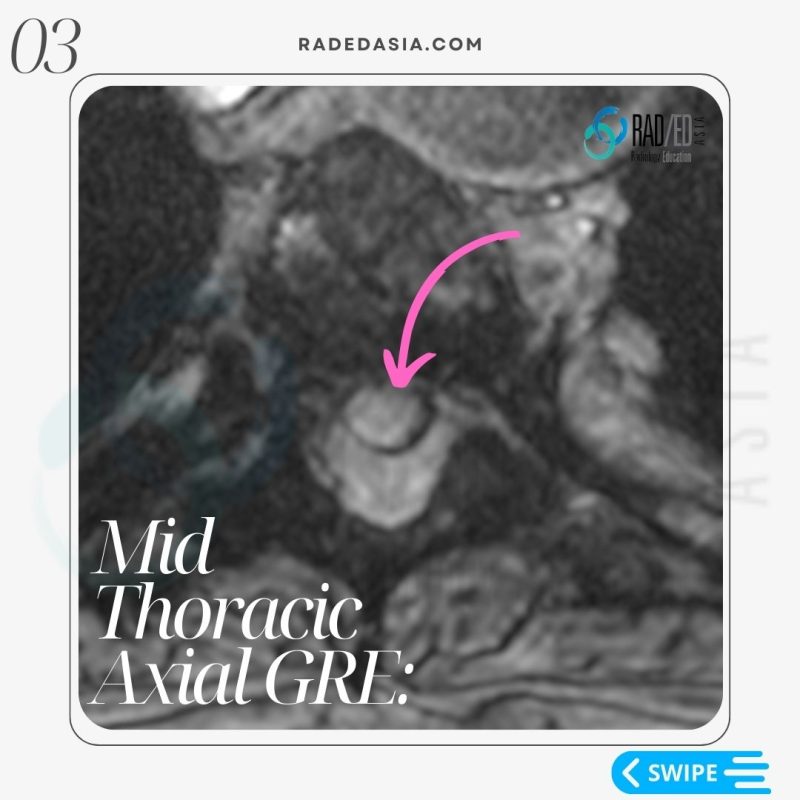
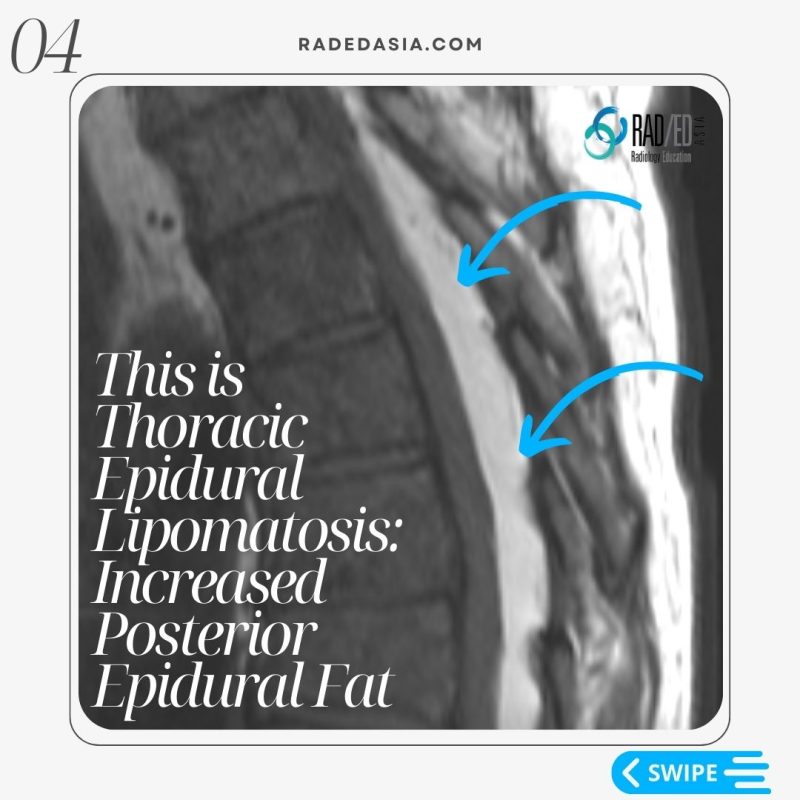
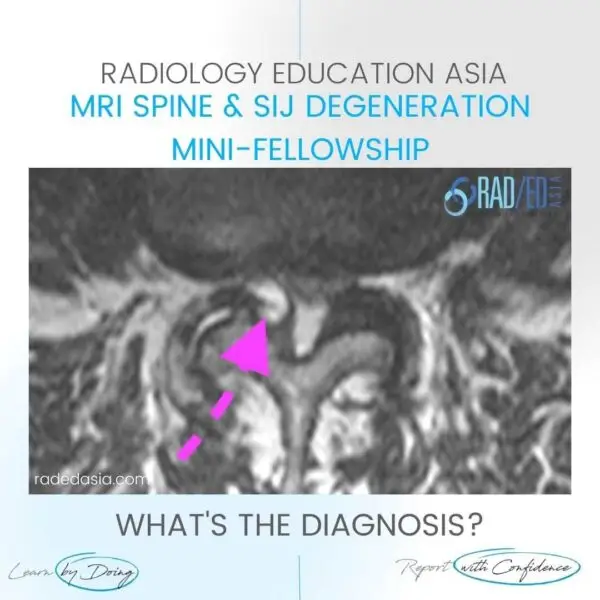
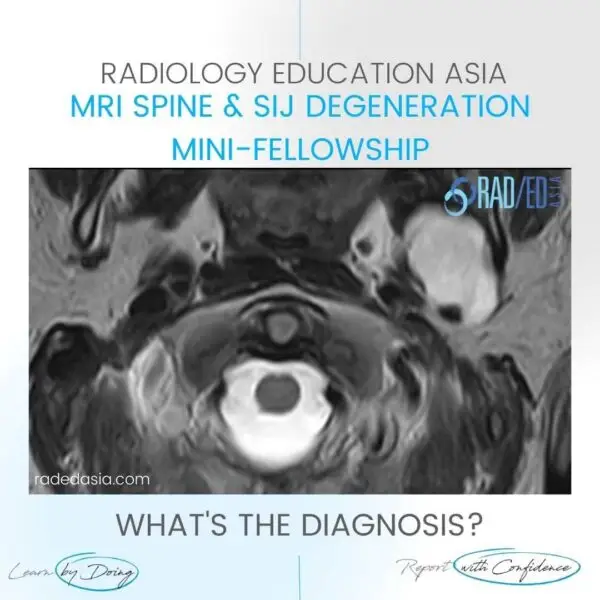
- Epidural lipomatosis in the thoracic spine has a different appearance to Lumbar Epidural Lipomatosis.
- In the lumbar spine we look for a trefoil appearance of the thecal sac.
- However, in the thoracic spine we look for Increased epidural fat.
- The fat accumulation is posterior and lateral.
- This results in the Cord being displaced anteriorly and thecal sac effaced.
- There is no trefoil appearance like you see in the lumbar spine.
THE TAKE AWAY
- Epidural lipomatosis in the thoracic spine has a different appearance to Lumbar Epidural lipomatosis (See Here).
- Look for increased fat in the epidural space and cord displacement.
THORACIC EPIDURAL LIPOMATOSIS: VIEW IMAGES
Learn more about this condition & how best to report it in more detail in our SPINE & SIJ Imaging Mini Fellowships.
Click on the image below for more information.
- Join our WhatsApp RadEdAsia community for regular educational posts at this link: https://bit.ly/radedasiacommunity
- Get our weekly email with all our educational posts: https://bit.ly/whathappendthisweek