This site is intended for Medical Professions only. Use of this site is governed by our Terms of Service and Privacy Statement which can be found by clicking on the links. Please accept before proceeding to the website.

MRI & ULTRASOUND: ACJ CYSTS AND GEYSER SIGN – DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING FINDINGS

ACJ CYSTS AND GEYSER SIGN - DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING FINDINGS

A combined Clinico Radiological case from Dr Joe Thomas (Rheumatologist)
This is a combined case with Dr Joe Thomas, a senior consultant Rheumatologist who is also joining us in presenting the Spine Arthropathy and Spondyloarthropathy course.
TYPES OF AC JOINT GANGLION CYSTS
OVERVIEW
TYPE 1 ACJ GANGLION CYSTS
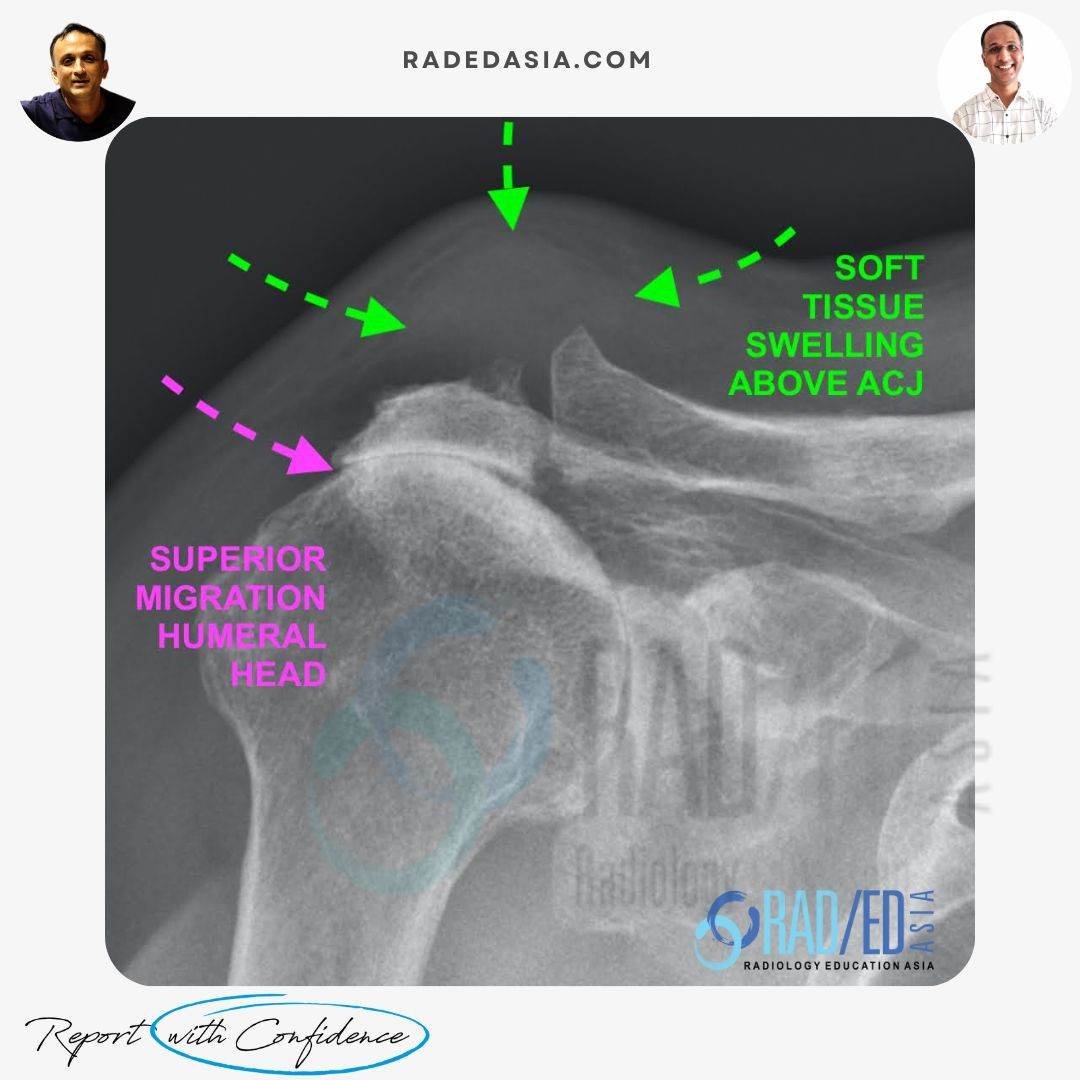
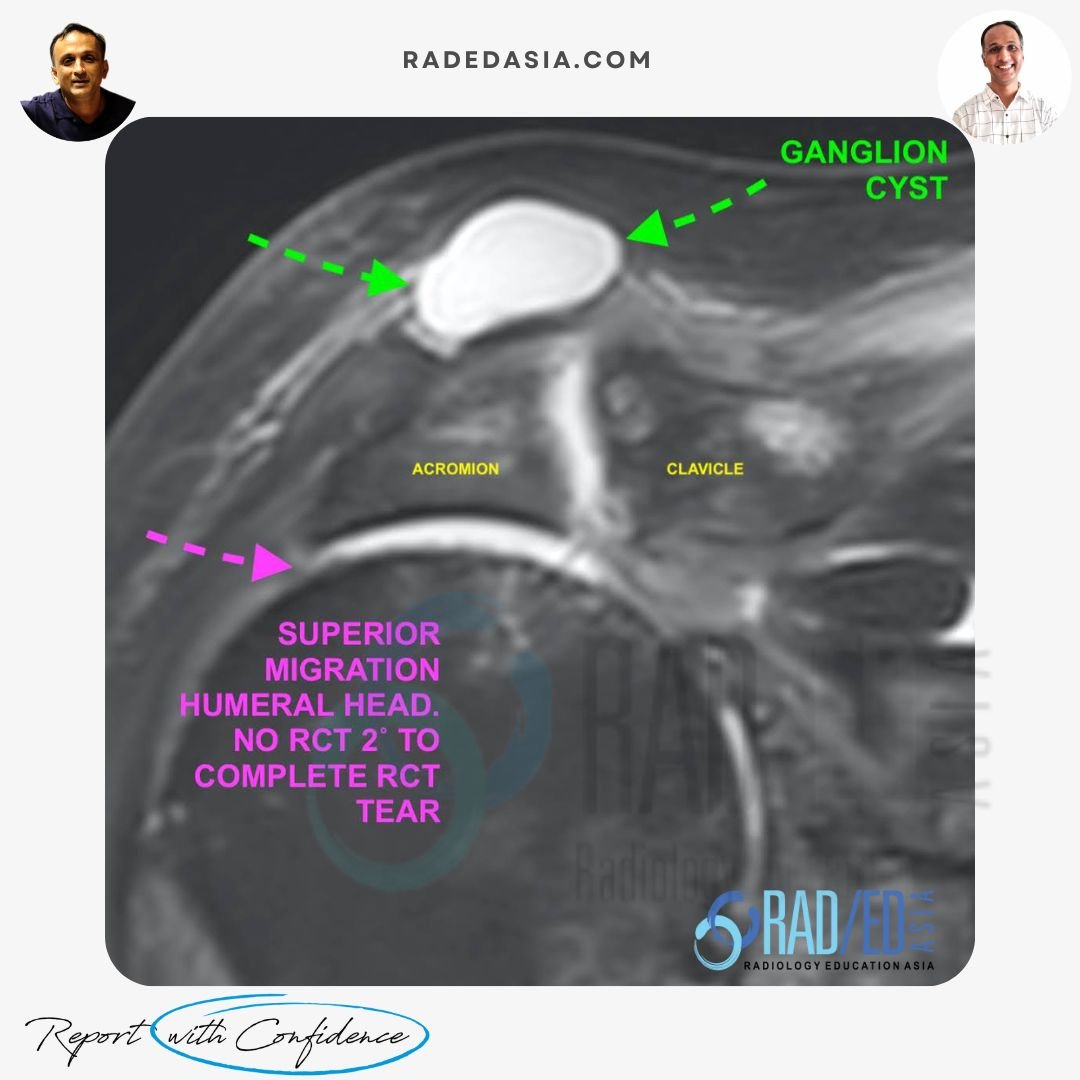
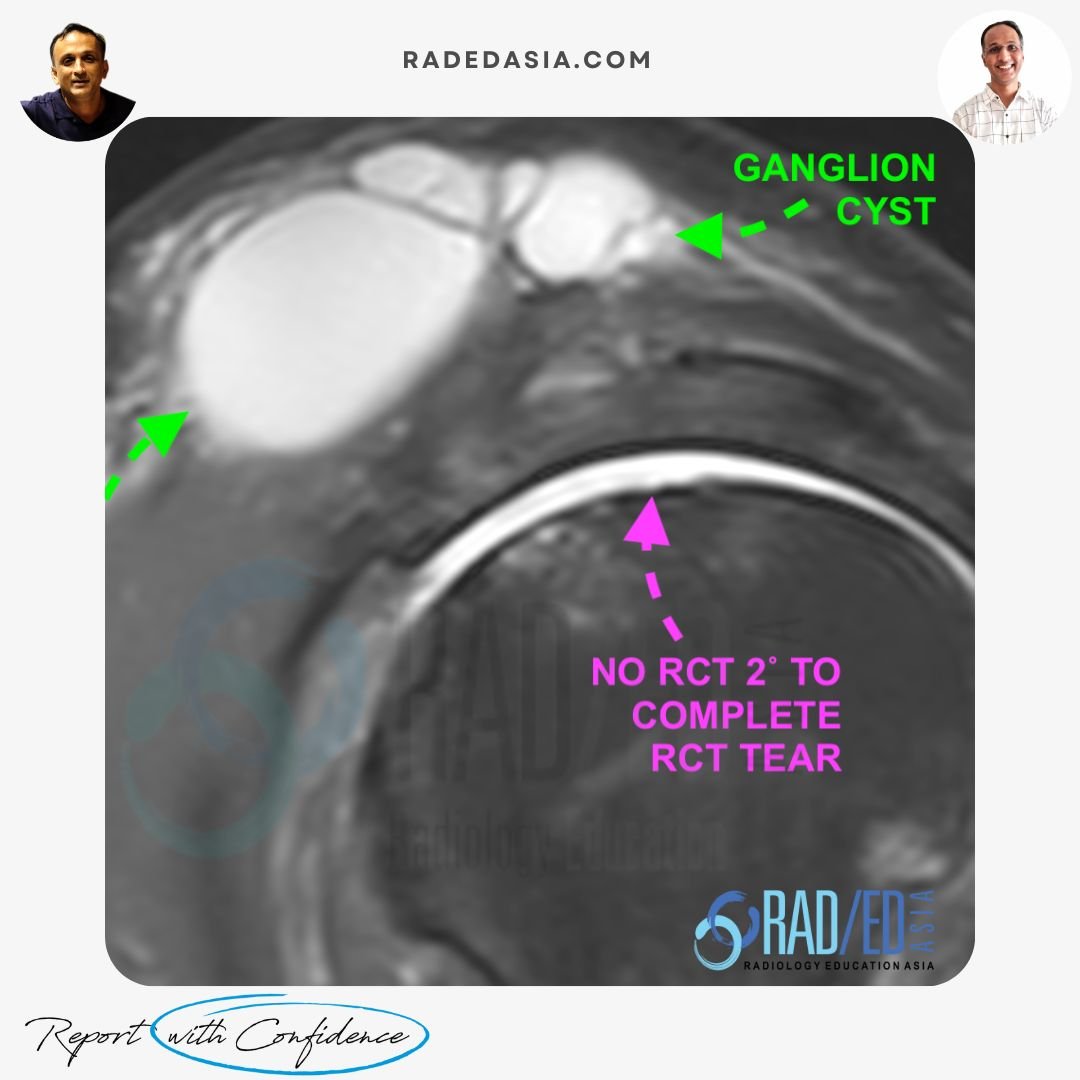
TYPE 2 ACJ GANGLION CYSTS (THIS CASE)
These cysts are associated with rotator cuff tears, usually complete tears. Complete RCT tears result in superior migration of the humeral head which erodes the ACJ capsule and fluid enters the ACJ from the Glenohumeral joint. There is also increased synovial fluid production in the ACJ. Eventually a tear in the superior margin of the ACJ capsule results in synovial fluid extension out of the AC joint, creating a ganglion cyst.
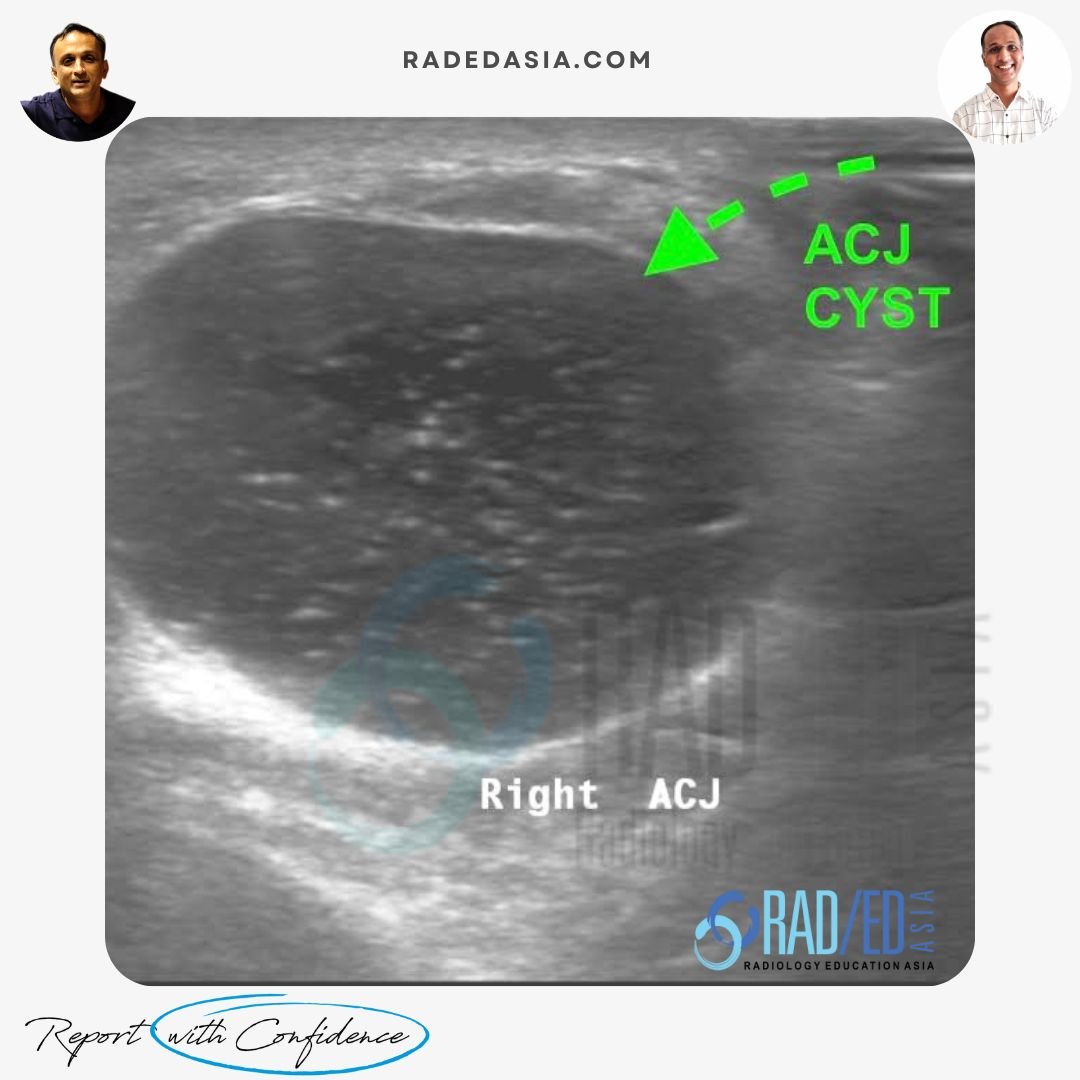
THE GEYSER SIGN
WHAT IS IT?
ULTRASOUND GUIDED ASPIRATION
KEY POINT
READ MORE
Read Article: “Acromioclavicular Joint Cyst Formation Clinical Anatomy“, Read HERE
TEST YOURSELF ON SOME COMMON & FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF TYPE 1 AC JOINT GANGLION CYSTS?
WHAT IS THE GEYSER SIGN?
- Join our WhatsApp RadEdAsia community for regular educational posts at this link: https://bit.ly/radedasiacommunity
- Get our weekly email with all our educational posts: https://bit.ly/whathappendthisweek