This site is intended for Medical Professions only. Use of this site is governed by our Terms of Service and Privacy Statement which can be found by clicking on the links. Please accept before proceeding to the website.
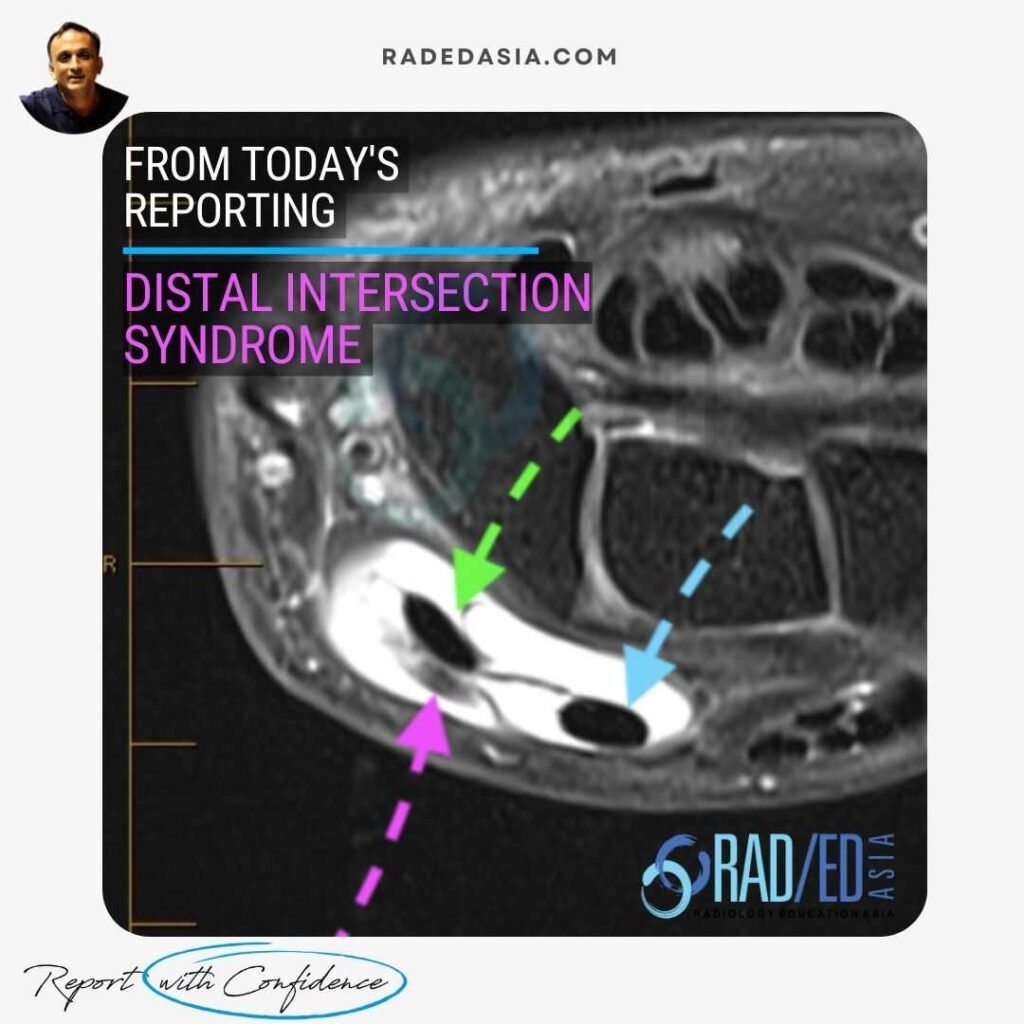
MRI WRIST IMAGING FINDINGS IN DISTAL INTERSECTION SYNDROME

MRI FINDINGS IN DISTAL INTERSECTION SYNDROME
CAUSE OF DISTAL INTERSECTION SYNDROME
Lister’s tubercle acts as a pulley for the EPL tendon, which changes its angle of course, leading it to cross superficially over the second compartment tendons.
This can lead to increased friction between the tendons.
There is ALSO a potential communication foramen between the second and third compartments, which can allow inflammation to spread between them.
FINDINGS IN THIS CASE
ADDITIONAL FINDINGS IN DISTAL INTERSECTION SYNDROME
There can also be additional findings of:
- Tendinosis, which can manifest as thickening and/or increased signal intensity within the involved tendons (EPL, ECRB, ECRL).
- Partial tendon tears.
- Reactive marrow oedema in adjacent bony structures, such as Lister’s tubercle.
- In severe cases, a complete tear and retraction of the EPL tendon.
EXTERNAL SOURCE FOR CITATIONS
Radsource – MRI Features of Distal Intersection Syndrome.
TEST YOURSELF ON SOME COMMON & FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
WHAT MRI FINDINGS INDICATE DISTAL INTERSECTION SYNDROME?
HOW IS PROXIMAL INTERSECTION SYNDROME DIFFERENT FROM DISTAL
HOW IS DISTAL INTERSECTION SYNDROME DIFFERENT FROM DE QUERVAIN’S TENOSYNOVITIS?
Our CPD & Learning Partners
- Join our WhatsApp RadEdAsia community for regular educational posts at this link: https://bit.ly/radedasiacommunity
- Get our weekly email with all our educational posts: https://bit.ly/whathappendthisweek