This site is intended for Medical Professions only. Use of this site is governed by our Terms of Service and Privacy Statement which can be found by clicking on the links. Please accept before proceeding to the website.
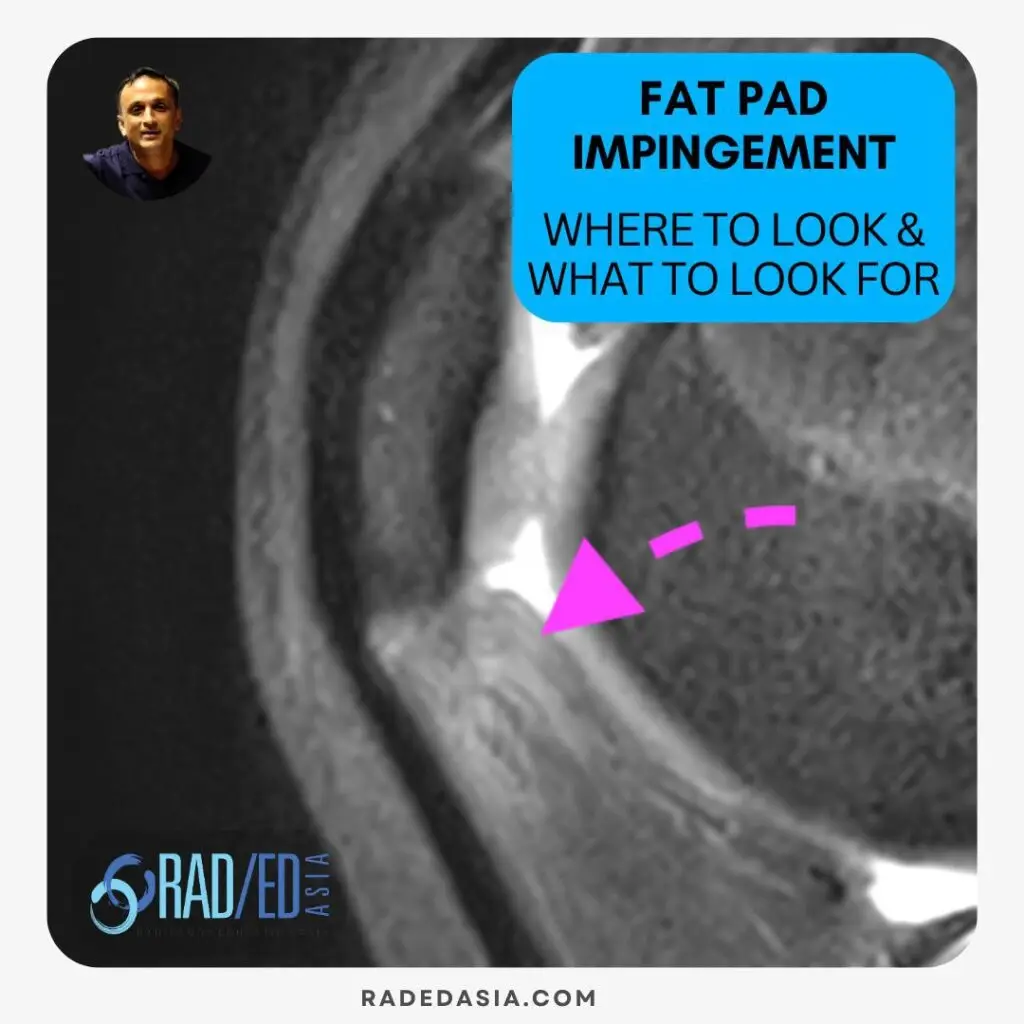
Knee fat pad impingement syndromes are characterized by pain and inflammation of the fat pads surrounding the knee joint and can significantly impact knee function.
This blog post looks at the anatomy of the knee fat pads, the MRI appearance of impingement, and key areas to focus on MRI, to make accurate a diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment decisions.
There are four fat pads around the knee that can become impinged and can be symptomatic.
Quadriceps fat pad:
Located above the patella and posterior to the quadriceps tendon.
Supratrochlear fat pad:
Situated anterior to the femoral trochlea.
Hoffa’s fat pad:
Positioned behind the patella/ patella tendon and tibia.

On MRI Impingement of any of the fat pads has a similar appearance and the best sequence to diagnose it is on a STIR/T2FS or PDFS sequence.
Look for
Increased signal intensity on fluid-sensitive sequences (PDFS, STIR, T2-weighted) in the affected fat pad.
Low signal intensity on T1-weighted images.
Edema may extend to surrounding soft tissues.

Image Above: Impingement of quadriceps fat pad (yellow arrow). Due to swelling the posterior margin can become convex (blue arrow).
Image Above: Impingement of supratrochlear fat pad (yellow arrow). Same appearance as impingement elsewhere.
Image Above: Impingement of Hoffa’s fat pad (yellow arrow).

Stay tuned on new
Mini-Fellowships launches and learnings
This site is intended for Medical Professions only. Use of this site is governed by our Terms of Service and Privacy Statement which can be found by clicking on the links. Please accept before proceeding to the website.