Lateralization of the tibial tubercle is one of the predisposing factors for Patellar Dislocation.
In this post we look at what the normal position is, how to measure lateralization and what the differences between CT and MRI measurements are.
NORMAL:
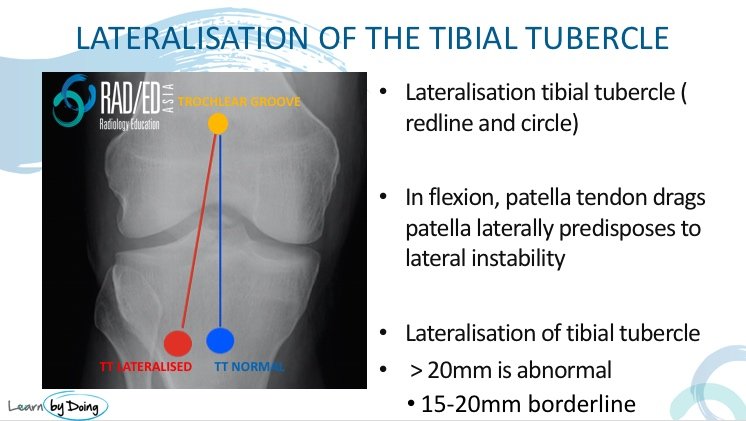
The normal tibial tubercle lies roughly in line with the apex of the trochlear groove and the course of the patella tendon from the inferior pole of the patella to the insertion on the tibial tubercle is relatively vertical. Thus in knee flexion the patella stays relatively midline.
LATERALISED:
The tibial tuberosity can be more laterally placed and this results in a oblique course of the patella tendon with resultant increased lateral force on the patella in flexion. This results in increased risk of lateral patella subluxation.
The measurements above are based on CT evaluation where the knee is in full extension.
However in MRI with a knee coil the knee is about 15 degrees of flexion which results in some medialisation of the tibial tubercle.
In MRI Normal is considered <15mm.
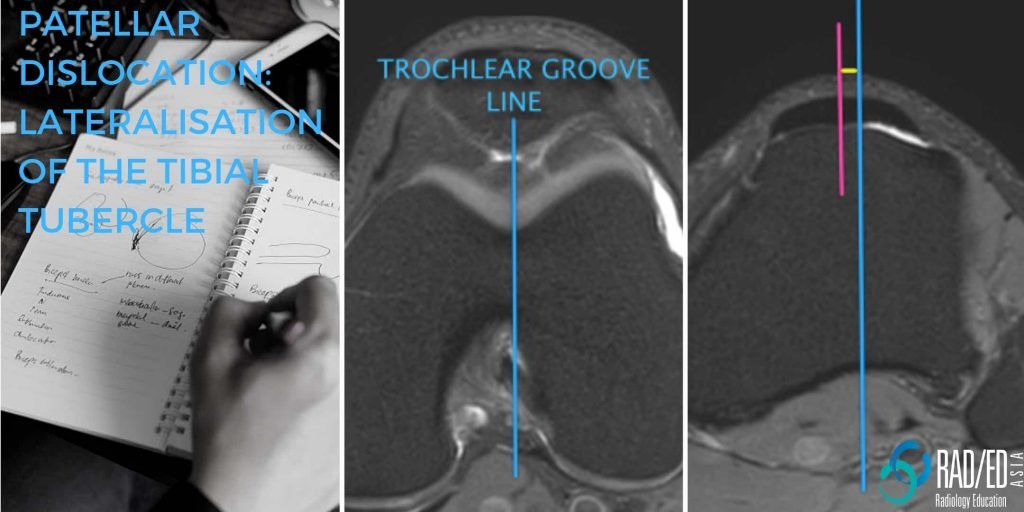
The transverse distance between the trochlear groove and the tibial tuberosity is called the TT-TG distance (Tibial Tuberosity Trochlear Groove distance).
- First line is through the apex of the deepest part of the trochlear groove (Blue line).
- Alternate level is most proximal level of trochlear groove.
- Second line is through the centre of the patella tendon at its attachment to the tubercle (Pink line)
- The TTTG distance (Yellow line) is the distance between the first two lines.
HOW DO YOU MEASURE IT ON A SCAN
- Place your cursor over the deepest part of the trochlear groove.
- Scroll down with the cursor not moving until you get to the patella tendon insertion.
- Measure the distance between where your cursor is and the centre point of the patella tendon at the attachment to the tibial tuberosity.
The TT-TG distance can vary between CT and MRI and also within MRIs depending on the position of the knee.
- The TT-TG distance increases at the end of extension. So if you use a body coil to scan the knee the knee will be fully extended and the TT-TG distance will be higher than if you use a dedicated knee coil where the knee is slightly in flexion.
- MRI will underestimate the TT-TG distance compared to CT as CT is done in full extension. (See above for measurements on CT and MRI).
(CT and MRI Measurements of Tibial Tubercle–Trochlear Groove Distances Are Not Equivalent in Patients With Patellar Instability American Journal of Sports Medicine Vol 41, Issue 8, 2013).
- Join our WhatsApp RadEdAsia community for regular educational posts at this link: https://bit.ly/radedasiacommunity
- Get our weekly email with all our educational posts: https://bit.ly/whathappendthisweek
#radedasia #mri #mskmri #radiology